Experimenting with Kubernetes on Multipass VMs
As part of my Kubernetes learning journey, I built a 3-node cluster entirely on top of a single Ubuntu machine.
This setup is, of course, a single point of failure, but it served well for experimentation and practice with kubeadm.
Cluster Setup
- Environment: One Ubuntu host machine.
- Virtualization: Multipass used to create lightweight VMs.
- VMs created:
k8s-control– control plane nodek8s-worker1– worker nodek8s-worker2– worker node
- Networking: Default Multipass bridge.
- Container Runtime:
containerd. - Cluster Init:
kubeadm initrun on the control plane, with workers joining via thekubeadm jointoken.
Architecture
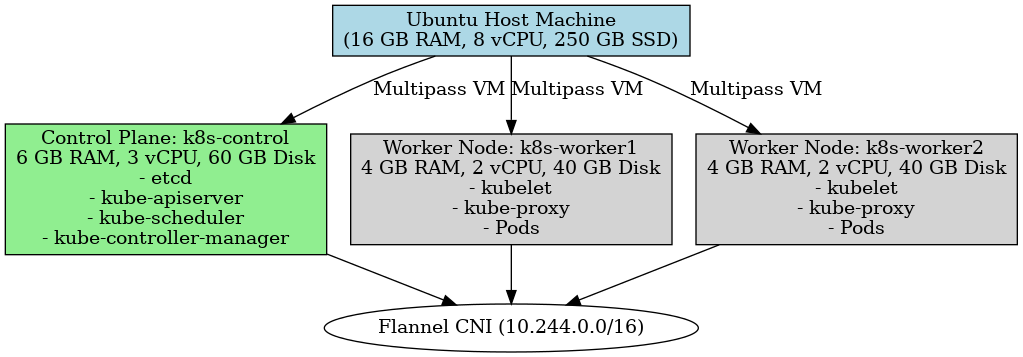
Diagram notes (as shown above)
- Ubuntu Host Machine — 16 GB RAM, 8 vCPU, 250 GB SSD (host system running Multipass).
- k8s-control (control plane VM) — 4 GB RAM, 2 vCPU, 50 GB disk: runs
etcd,kube-apiserver,kube-scheduler,kube-controller-manager. - k8s-worker1 (worker VM) — 2 GB RAM, 1 vCPU, 30 GB disk: runs
kubelet,kube-proxy, container workloads. - k8s-worker2 (worker VM) — 2 GB RAM, 1 vCPU, 30 GB disk: runs
kubelet,kube-proxy, container workloads. - CNI — Flannel (
10.244.0.0/16) connecting all nodes.
Challenges Faced
Bringing up the cluster was not smooth — I encountered several recurring problems:
kubectl get nodesfailed withconnection refusedon port6443.- Control-plane static pods (
etcd,kube-apiserver,kube-controller-manager,kube-scheduler) repeatedly went intoCrashLoopBackOff. crictl ps -arevealed containers constantly starting and exiting.- Logs (
journalctl -u kubelet) showed:node "k8s-control" not found- Issues with containerd socket (
/var/run/containerd/containerd.socknot found) - Errors creating mirror pods for
etcdandkube-apiserver
- Applying Flannel CNI initially failed because the API server was not reachable.
Troubleshooting Journey & Summary of Work
I documented the exact commands and state while bringing the cluster up — below is a concise summary of what I did, and how I approached the failures.
What I built
- Created three Multipass VMs on a single Ubuntu host: one control-plane and two workers.
- Installed and configured
containerd,kubeadm,kubelet, andkubectl. - Initialized the control plane with
kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16. - Joined workers using the
kubeadm jointoken. - Deployed Flannel CNI to provide pod networking.
Troubleshooting steps I performed (chronological)
- Runtime and container checks
sudo crictl ps -ato list containers and their states.- Noted repeated restarts and exit codes for
etcdandkube-apiserver.
- Log inspection
sudo journalctl -u kubelet -n 200 --no-pagerto inspect kubelet problems (mirror pod creation, sandbox errors, token fetch failures).sudo crictl logs <container-id> --tail 200for etcd and kube-apiserver logs; journalctl for containerd logs.
- Container runtime health
- Restarted
containerdandkubeletwhen the container runtime socket was missing or shims were stuck:sudo systemctl restart containerd sudo systemctl restart kubelet - Cleaned up stuck
containerd-shimprocesses when necessary (killed long-dead shims).
- Restarted
- Fixed crictl config
- Ensured
/etc/crictl.yaml(or default endpoints) pointed tounix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock.
- Ensured
- Detected deadlock
- Observed the
etcd↔kube-apiserverdeadlock: when etcd failed, API server couldn’t start; when API server was down kubelet couldn’t register the node or provide tokens for CNI pods.
- Observed the
- Rebuild
- After long diagnostic attempts and intermittent fixes, I created a fresh VM with higher resources for control plane, reinstalled packages, reinitialized the cluster, and redeployed the CNI — which resolved the instability faster than trying to salvage the corrupted state.
Key commands used (examples)
# show container runtime status
sudo systemctl status containerd
sudo crictl ps -a
# kubelet logs
sudo journalctl -u kubelet -n 200 --no-pager
# inspect static pod logs (for control-plane components)
sudo crictl logs <ETCD_CONTAINER_ID> --tail 200
sudo crictl logs <APISERVER_CONTAINER_ID> --tail 200
# reconfigure/crictl endpoint if needed
sudo tee /etc/crictl.yaml <<EOF
runtime-endpoint: unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock
EOF
# restart services
sudo systemctl restart containerd kubelet
# deploy CNI (after API server healthy)
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
